About the Journal

Vectors claim its importance in biological sciences, especially with relation to particular disease transmission and molecular biology aspects. Vector is any agent (person, animal, or microorganism or extra-chromosomal DNA) that carry and transmits the disease or gene into another living organism.
Global expenditure on research in understanding its biology of the vector is increasing every year due to the re-emergence of several infectious diseases including Malaria, Dengue, Chikungunya, West Nile virus, Plant related disease etc. Observing such need of latest information for the global research community and public, Vector Biology Journal is launched with the aim of dissemination of useful scientific knowledge.
About the journal
Vector Biology Journal is a completely open access which is accepted timely articles from all over the world. This periodical publishes different types of articles including research articles, review, case reports, commentary, letter to an editor, mini review, opinion, short communication, book review, editorials and methodology articles on the latest updates on the subject.
The journal aims to provide a common platform to the global research community, academicians, individuals and the agencies that work on public health issues to harness and participate in a meaningful discussion on topics related to vector-borne diseases, pathophysiology. The objective of this journal is to spread awareness on the subject that will be beneficial to the mankind.
Topics Covered
Vector Biology Journal majorly considers the following topics mentioned in the following section but the journal is not limited to such topics. The Vector Biology Journal focuses on the theme of taxonomical studies of organism which are responsible for the causing diseases and understanding the biology of the vectors, vector competence and biological control of vector, vector–parasite interaction, epidemiology, parasitology, surveillance, technology involved in controlling of vectors and biopesticides, insecticides in vector controlling management, to study of relation between the reservoir host and vector host, genomics and proteomics studies associated with vector biology.
Submission of Papers
The journal accepts Research articles emphasising on Empirical evidence, Review Articles, Case Reports, Mini Reviews, Commentaries, Letters to the Editor, Scientific Reports, Thesis and Clinical images etc. To avail, the complete information on manuscripts submission click here
Processing of Manuscripts
Vector Biology follows a double blind peer reviewed policy and review process is performed by editorial board members of the journal and two other research eminent. At least two independent reviewers approval followed by the editor decision is mandatory for the acceptance of any citable manuscript.
Submit your manuscript at Online Submission System
Submit Manuscripts as e-mail attachment to the Editorial Office at manuscripts@scitechnol.com
Pathogens
In biological term, a pathogen term often used for the agents to which disrupt the normal function of the any organism that can produce disease. Typically the term is used to describe an infectious agent such as a virus, bacterium, prion, a fungus, or even another micro-organism.
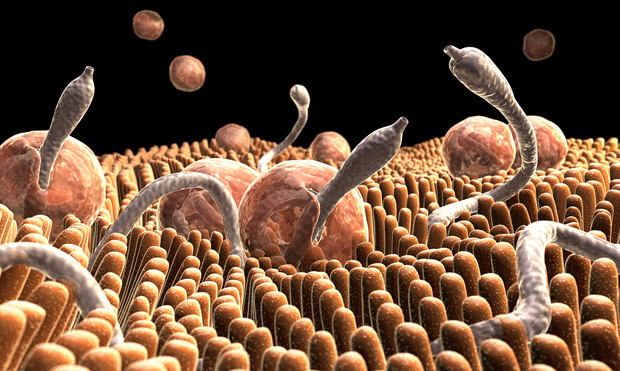
Vector
Vector is a carrier, which carries the parasitic agents. For example, malaria mosquito serves as the vector that carries and transfers the infectious agent (Plasmodium), injecting it with a bite and spread the diseases. Vector only acts as a source for transmission of the diseases.
Parasite-Host Response
The parasite-host response is the process by which a host interacts with and responds to parasites that it encounters. It includes various mechanisms, including immune mechanisms that are elicited in an attempt to eliminate the parasite or halt its growth.
Vector Competence
Vector competence is an evaluation of the vector’s capability (mechanism) to transmit a pathogen. The molecular characterization of genes that influence vector competence is becoming routine, and with the development of the Sindbis virus transducing system, potential antipathogen genes now can be introduced into the mosquito and their effect on parasite development can be assessed in vivo.
Vectorial Capacity
Vectorial Capacity is a measurement of the efficiency of vector-borne disease transmission.Vector competence is an evaluation of the vector’s capability (mechanical or biological) to transmit a pathogen. Therefore, vector competence is actually an additional component of vectorial capacity.
Vector-Parasite Interaction
Vector-Parasite Interaction is quite similar to host-virus interaction which helps to investigate the contribution of understanding the genetic variation of some mosquitoes better than others at transmitting malaria parasites to humans.
Vector Ecology
Vector Ecology has a primary emphasis is on the epidemiology of vector-borne diseases and the bionomics, control of disease vectors. Ecology of vector helps to plan and implement prevention and control measures to protect deployed forces from disease, injury, and annoyance caused by vectors and pests.
Vector Borne Diseases
Vector-borne diseases are infections which are transmitted by the bite of infected arthropod species acting as a vector, such as mosquitoes, ticks, triatomine bugs, sand flies, and blackflies. Arthropod vectors are cold-blooded (ectothermic) and thus especially sensitive to climatic factors.
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease of humans and other animals caused by parasitic protozoans. 2013 an estimated 198 million cases register of vector-borne diseases worldwide and 500,000 people died, mostly children.
Tick-borne diseases
Tick-borne diseases, which carry the pathogen that can cause humans diseases which are transmitted through the bites by ticks. Tick-Borne Diseases
Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is a disease caused by a family of viruses that are transmitted by mosquitoes. Symptoms include severe joint and muscle pain, swollen lymph nodes, headache, fever, exhaustion, and rash. The presence of fever, rash, and headache (the "dengue triad") is characteristic of dengue fever. Dengue is prevalent throughout the tropics and subtropics.
Chikungunya
Chikungunya is a viral disease transmitted to humans by infected mosquitoes. It causes fever and severe joint pain. Other symptoms include muscle pain, headache, nausea, fatigue and rash.Chikungunya outbreaks are usually recorded within an interval of 7-8 years. Between 1960 and 1980 a number of outbreaks were reported from Asia and Africa. It made a comeback in recent years and is now being reported regularly from India, Indonesia, Maldives and Thailand. In 2006, a large outbreak of Chikungunya was reported from La Réunion Island (France) with estimates of over 100,000 people infected and 200 deaths. In 2010, many cases were reported from Delhi. Due to its non-fatal nature, a large number of Chikungunya infections go unreported.
Integrated Vector Management
Integrated Vector Management is a rational decision-making process for the optimal use of resources for vector control.The most frequent type of vector control is mosquito control using a variety of strategies.Vector control focuses on utilising preventative methods to control or eliminate vector populations.
Reservoir Competence
Reservoir Competence is the ability of a host infected with the pathogen to make the pathogen available for the vector. It can determine by Infectivity-timing with vector activity, an abundance of the reservoir - Contribution to infection in the vector (proportion of vectors that feed on the reservoir that becomes infected with the pathogen and host immunity.
Vector Surveillance & Control
Entomological surveillance is used to determine changes in the geographical distribution and density of the vector, evaluate control programmes, obtain relative measurements of the vector population over time and facilitate appropriate and timely decisions regarding interventions.
Fast Editorial Execution and Review Process (FEE-Review Process):
Vector Biology Journal is participating in the Fast Editorial Execution and Review Process (FEE-Review Process) with an additional prepayment of $99 apart from the regular article processing fee. Fast Editorial Execution and Review Process is a special service for the article that enables it to get a faster response in the pre-review stage from the handling editor as well as a review from the reviewer. An author can get a faster response of pre-review maximum in 3 days since submission, and a review process by the reviewer maximum in 5 days, followed by revision/publication in 2 days. If the article gets notified for revision by the handling editor, then it will take another 5 days for external review by the previous reviewer or alternative reviewer.
Acceptance of manuscripts is driven entirely by handling editorial team considerations and independent peer-review, ensuring the highest standards are maintained no matter the route to regular peer-reviewed publication or a fast editorial review process. The handling editor and the article contributor are responsible for adhering to scientific standards. The article FEE-Review process of $99 will not be refunded even if the article is rejected or withdrawn for publication.
The corresponding author or institution/organization is responsible for making the manuscript FEE-Review Process payment. The additional FEE-Review Process payment covers the fast review processing and quick editorial decisions, and regular article publication covers the preparation in various formats for online publication, securing full-text inclusion in a number of permanent archives like HTML, XML, and PDF, and feeding to different indexing agencies.